qrisp.gqsp.fourier_series_loader#
- fourier_series_loader(qarg: QuantumVariable, signal: ArrayLike | None = None, frequencies: ArrayLike | None = None, k: int = 1, mirror: bool = False) QuantumBool[source]#
Performs quantum state preparation for the first \(k\) Fourier modes.
Given an input array of \(M\) values \(\{a_{j}\}_{j=0}^{M-1}\) representing a signal sampled at equidistant points, this method prepares an \(n\)-qubit quantum state \((N=2^{n})\) by reconstructing a smooth approximation of the signal using its lowest \(2k+1\) frequency components.
First, the method computes the frequency coefficients \(c_{l}\):
\[c_l = \frac{1}{M}\sum_{j=0}^{M-1} a_j e^{-i \frac{2\pi jl}{M}}\]The method prepares the \(n\)-qubit state:
\[\ket{\psi} = \sum_{m=0}^{N-1} \psi_m \ket{m}\]where the amplitudes \(\psi_{m}\) are computed using a band-limited inverse transform:
\[\psi_m = \frac{1}{\mathcal{K}}\sum_{l=-k}^k c_l e^{i \frac{2\pi lm}{N}}\]In this expression, \(\mathcal{K}\) is a normalization constant ensuring \(\sum |\psi _{m}|^{2}=1\).
- Parameters:
- qargQuantumVariable
Variable representing the input signal. Must be in state \(\ket{0}\) for preparation of target signal.
- signalArrayLike, shape (M,), optional
The target signal values. Either
signalorfrequenciesmust be specified.- frequenciesArrayLike, shape (2K+1), optional
The target frequency values in the range \([-K,K]\).
- kint
The frequency cutoff. Only frequencies in the range \([-k,k]\) are preserved. The default is 1.
- mirrorbool
If True, frequencies are caluclated from mirror padded
signalvia FFT to mitigate artifacts at the boundaries. The default is False.
- Returns:
- QuantumBool
Auxiliary variable after applying the GQSP protocol. Must be measured in state \(\ket{0}\) for the GQSP protocol to be successful.
Notes
This method is particularly useful for preparing smooth states or approximating continuous functions where high-frequency noise should be filtered out.
If (2k+1=M=N), this reduces to a standard state preparation from a full DFT.
Examples
We prepare a quantum state with amplitudes following a Gaussian distribution.
# Restart the kernel to enable high-precision simulation import os os.environ["QRISP_SIMULATOR_FLOAT_THRESH"] = "1e-10" import jax.numpy as jnp import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from qrisp import * from qrisp.gqsp import fourier_series_loader # Gaussian def f(x, alpha): return jnp.exp(-alpha * x ** 2) # Converts the function to be executed within a # repeat-until-success (RUS) procedure. @RUS(static_argnames=["k"]) def prepare_gaussian(n, alpha, k): # Use 32 sampling points to evaluate f N_samples = 32 x_val = jnp.arange(-1.0, 1.0, 2.0 / N_samples) y_val = f(x_val, alpha) y_val = y_val / jnp.linalg.norm(y_val) qv = QuantumFloat(n) anc = fourier_series_loader(qv, y_val, k=k) success_bool = measure(anc) == 0 reset(anc) anc.delete() return success_bool, qv # The terminal_sampling decorator performs a hybrid simulation, # and afterwards samples from the resulting quantum state. @terminal_sampling def main(n, alpha): qv = prepare_gaussian(n, alpha, 3) return qv # Run the simulation for n-qubit state n = 6 alpha = 4 res_dict = main(n, alpha) y_val_sim = np.sqrt([res_dict.get(key, 0) for key in range(2 ** n)]) # Compare to target amplitudes x_val = np.arange(-1, 1, 2 ** (-n + 1)) y_val = f(x_val, alpha) y_val = y_val / np.linalg.norm(y_val) plt.scatter(x_val, y_val, color='#20306f', marker="d", linestyle="solid", s=20, label="target") plt.plot(x_val, y_val_sim, color='#6929C4', marker="o", linestyle="solid", alpha=0.5, label="qsp") plt.xlabel("x", fontsize=15, color="#444444") plt.ylabel("Amplitudes f(x)", fontsize=15, color="#444444") plt.legend(fontsize=15, labelcolor='linecolor') plt.tick_params(axis='both', labelsize=12) plt.grid() plt.show()
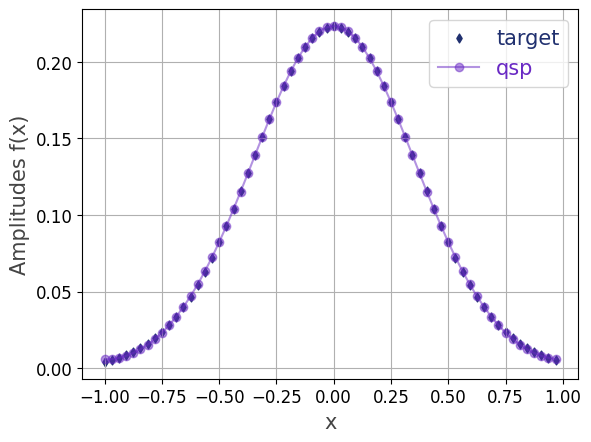
To perform quantum resource estimation, replace the
@terminal_samplingdecorator with@count_ops(meas_behavior="0"):@count_ops(meas_behavior="0") def main(n, alpha): qv = prepare_gaussian(n, alpha, 3) return qv main(6, 4) # {'h': 6, 'rz': 8, 'p': 108, 'x': 6, 'cx': 72, 'rx': 7, 'measure': 1}
